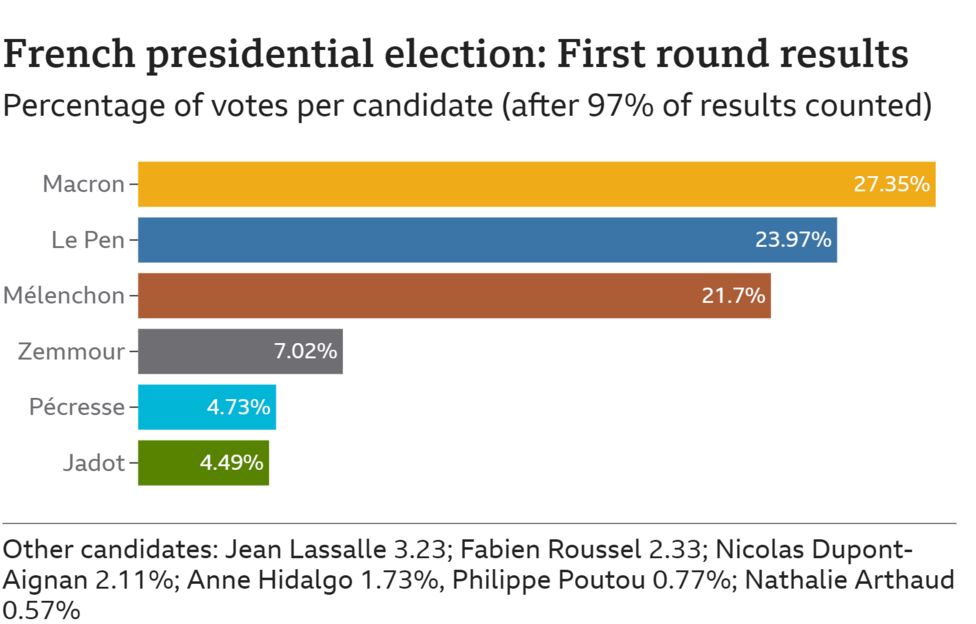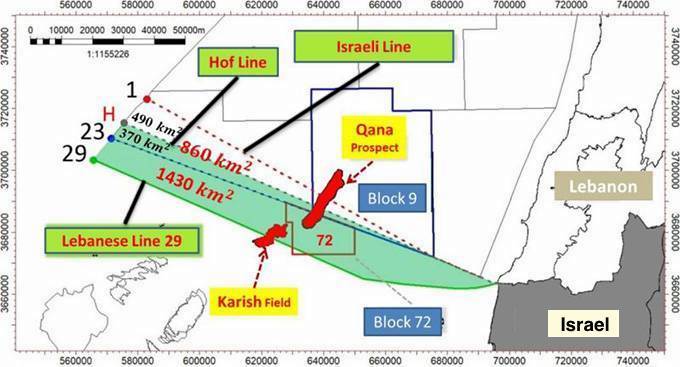
By Nicholas Noe — responsiblestatecraft.org — When President Biden appointed his personal friend and former Obama administration energy coordinator Amos Hochstein as his own energy envoy last summer, it seemed that the decades-old deadlock between Lebanon and Israel over their sea boundary, and potentially tens of billions of dollars in energy resources, might finally be resolved. Hochstein was assumed to be trusted by the Israelis (he was born in Israel and served in the IDF in the early 1990s). He was perceived positively by some of the main Lebanese actors as a foe of a former U.S. envoy, Ambassador Frederic Hof, who had tabled a deal ten years before known as the “Hof Line” boundary that was widely seen in Lebanon as exceptionally unfair. And he came with a deep background in the complexities of the energy sector.
Perhaps most importantly, however, the Biden administration seemed hungry to claim a success in the Arab-Israeli conflict. Although a mutually agreed-upon sea boundary between Lebanon and Israel would fall far short of any Abraham Accord-type arrangement, such a deal would represent a UN-recognized boundary between a democratically elected Arab government and Israel. Given the extensive power of the armed Lebanese political party Hezbollah, which Israel considers its most formidable non-state enemy, the removal of a large offshore area from the regular military exchanges between the two sides onshore would also help to structurally diminish the prospects of another devastating war in the Middle East, something the Biden administration very much wants to avoid.
Unfortunately, eight months on, according to several senior Lebanese officials directly involved in the negotiations, the deal that Hochstein unveiled a few weeks ago in Beirut, one which apparently has Israel’s blessing, falls far short of Lebanon’s minimum acceptable position. As a result, the talks are in imminent danger of collapsing, perhaps in the coming weeks. Asked about this prospect, the State Department and U.S. Embassy in Beirut both declined to comment.